11 Best Cybersecurity Certifications in 2023
This is a list of the best cybersecurity certifications that can boost your career in the cybersecurity field.
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting networks, computers, programs, and data from unauthorized access. This includes both cyber attacks and physical attacks.
Cybersecurity professionals work to prevent these attacks by identifying, analyzing, and responding to security threats.
If you are looking for a cybersecurity certification to take, now is the time.
Research from (ISC)^2 shows a global shortage of 4.07 million cybersecurity professionals.
Cybersecurity certification can help you learn and validate your skills in the cybersecurity field. Studies show that certified professionals are more likely to be employed and earn 10 to 20 percent higher salaries than those without certification.
Certification Criteria
For this list, I considered the following criteria:
- Development Standards - Developed based on a set process that is regulated by a standard organization.
- Availability of training materials Many training materials to help you prepare for the certification.
- Reputation - Held in high regard by those in the cybersecurity community.
- Applicability - The certification applies to a wide range of IT industries.
- Employer recognition: The certification is mentioned in many job postings
According to the above criteria, the best cyber security certifications are:
1. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Best cybersecurity certificate

The CISSP credential is the most respected certification in cybersecurity. Earning this certification shows your knowledge and skill in the field, which can help you advance your career and become part of a community of leaders in cybersecurity.
CISSP is a very difficult certification to get. The reported passing rate is between 50 to 70%. But, it is worth the effort because CISSP holders earn an average salary of $138,647.
CISSP features
| Cost | $749 |
| Exam duration | 6 hours |
| Number of questions | 250 |
| Passing grade | 700/1000 |
| Valid for | 3 years |
| Requirements | 5 years of experience |
| Standard | ISO/IEC Standard 17024 |
CISSP Domains
CISSP covers 8 domains:
- Security and Risk Management
- Asset Security
- Security Architecture and Engineering
- Communication and Network Security
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Security Assessment and Testing
- Security Operations
- Software Development Security
CISSP roadmap
To become a Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), you must have at least five years of experience working in information security positions. But don't worry if you don't have five years of experience. You can become an Associate of (ISC)² by passing the CISSP examination.
2. Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
Best penetration testing cybersecurity certificate
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) is a hands-on, practical certification that tests your ability to conduct a professional penetration test.
The OSCP is advanced cybersecurity certification for security professionals who have a strong technical and ethical hacking background, and know a lot about TCP/IP networks.
Being an offensive security professional is one of the hardest jobs in cybersecurity. In Professional Red Teaming, cybersecurity expert Dr. Jacob Oakley explains the role of an offensive security professional:
As offensive security professionals, we conduct our business by having to outsmart, fool, or otherwise identify shortcomings of our customers' organizations, and hope they are still willing to bring us back after being embarrassed.
OSCP features
| Cost | $1140 |
| Exam duration | 24 hours |
| Number of questions | 5 machines |
| Passing grade | 70/100 |
| Valid for | No expiration |
| Requirements | None |
OSCP roadmap
To earn the OSCP certification, you first need to complete a training course called "Offensive Security Certified Expert (OSCE)". This course will teach you the skills you need to pass the OSCP exam.
The OSCP exam is notoriously difficult. Candidates must pass a 24-hour exam where they are required to attack and penetrate live machines in a safe lab environment. After that, they must also submit a comprehensive penetration test report.
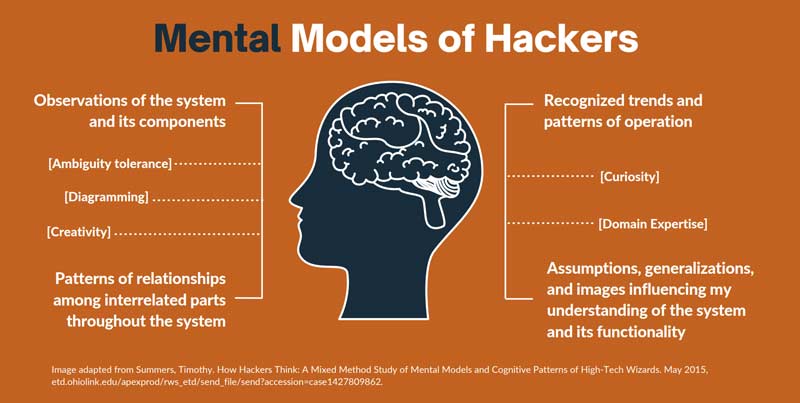
Image based on
A Study of Cybersecurity Experts and Their Mental Models
OSCP domain
OSCP doesn't have specific domains, but the practical skills include:
- Linux and Windows Environment
- Basic Programming Skills
- Web application attacks
- Metasploit Framework
- Nmap
- Netcat and Ncat
- Wireshark and tcpdump
- Windows and Linux Privilege Escalation
If you want to learn more about ethical hacking, check out my review of best ethical hacking books to help you get started.
3. Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
Best cybersecurity certification for managers

Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) is a management-focused certification that shows your ability to manage and oversee an information security program.
The CISM credential is for leaders of Cyber Security teams, or IT professionals, responsible for developing best organizational security practices. For example, it covers information security program development and management, which are vital for an organization's success, as mentioned in Roadmap to information security.
CISM is worth your time and effort because CISM holders earn an average salary of $118,000.
To qualify for the CISM credential, you must pass a written exam, have at least 5 years of security experience, and submit a written application.
CISM features
| Cost | $575 member/ $760 non-member |
| Exam duration | 4 hours |
| Number of questions | 150 |
| Passing grade | 450/800 |
| Valid for | 5 years |
| Requirements | 5 years of experience |
| Standard | ISO/IEC Standard 17024 |
CISM Domains
- Information Security Governance
- Information Risk Management and Compliance
- Information Security Program Development and Management
- Information Security Incident Management
4. GIAC Information Security Fundamentals (GISF)
Best cybersecurity certification for beginners

GISF is an introductory-level certification that is a good starting point for those new to the cybersecurity field.
GISF tests how well you know the basics of security, computer functions and networking, and cryptography.
Global Information Assurance Certification (GIAC) is worth your time if you are a beginner in the cyber security world, a manager, or an auditor. The certification shows that you have the basic knowledge needed to work in the field.
GISF features
| Cost | $999 |
| Exam duration | 2 hours |
| Number of questions | 75 |
| Passing grade | 72% |
| Valid for | 5 years |
| Requirements | None |
| Standard | ISO/IEC Standard 17024 |
GISF Domain
GISF cybersecurity certificate covers:
- Cyber security terminology
- The basics of computer network
- Security policies
- Incident response
- Passwords
- Introduction to cryptographic principles
5. Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
Best certificate for IT auditors

The CISA certification validates that a candidate has the experience, skills, and knowledge to assess vulnerabilities and compliance within an enterprise.
Being a successful IT auditor takes a lot of credibility and trust. The CISA certification is valuable because it helps you build both. The CISA certification is one of the most popular and respected certifications in the industry.
Compared to the other certifications on this list, the CISA is less technical and more focused on business processes.
To earn the CISA credential, you must pass a written exam and have at least 5 years of experience in information security or auditing.
CISA features
| Cost | $575 members / $760 non-members |
| Exam duration | 4 hours |
| Number of questions | 150 |
| Passing grade | 450/800 |
| Valid for | 4 years |
| Requirements | 5 years of experience |
| Standard | ISO/IEC Standard 17024 |
CISA domain
CISA certification covers the following topics:
- Auditing Information Systems
- Governance And Management Of IT
- Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Implementation
- Information Systems Operations, Maintenance, and Service Management
- Protection Of Information Assets
6. CompTIA Security+
CompTIA Security+ is an entry-level cybersecurity certification.
The CompTIA Security+ exam will certify that the successful candidate knows how to install and configure systems to secure applications, networks, and devices. They will also be able to perform threat analysis and respond with mitigation techniques.
CompTIA Security+ audience
The CompTIA Security+ certification is designed for people who work in IT and have at least two years of experience in this field. They should also have a good understanding of different security concerns, as well as how to implement security measures.
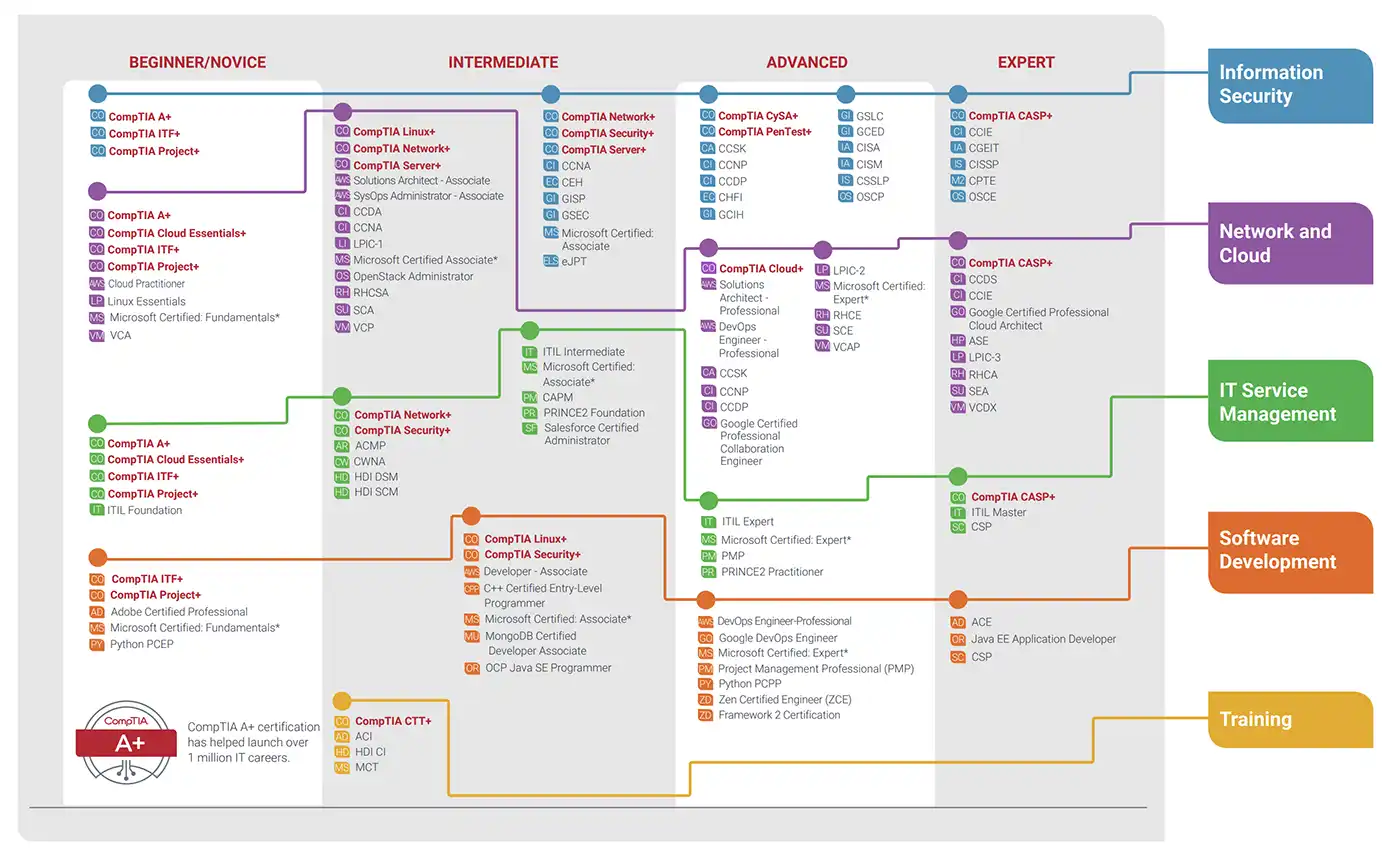
Domain
The certification domain covers:
- Threats, Attacks and Vulnerabilities 21%
- Technologies and Tools 22%
- Architecture and Design15%
- Identity and Access Management 16%
- Risk Management 14%
- Cryptography and PKI 12%
CompTIA Security+ features
| Cost | $381 |
| Exam duration | 90 minutes |
| Number of questions | 90 |
| Passing grade | 750/900 |
| Valid for | 3 years |
| Requirements | 2 years of experience |
7. Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
Best cybersecurity certification for ethical hackers

The Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) is an intermediate, vendor-neutral certification. CEH's mission statement is to help people protect their information by thinking like hackers.
This certification is a good way to learn about ethical hacking, including how to find vulnerabilities, how to penetrate systems, and more.
CEH features
| Cost | $1199 |
| Exam duration | 4 hours |
| Number of questions | 125 |
| Passing grade | 60-80% |
| Valid for | 3 years |
| Requirements | 2 years of experience |
Who is CEH for?
CEH is for security practitioners with hands-on experience. This certification is for people who want to be security officers, IT auditors, or site administrators. If you want to move into a management role, or if you're already in management, this certification is not for you.
CEH domains
Certified Ethical Hacker certificate is worth it if you are looking for a vendor-neutral certification that covers a wide range of topics, such as:
- Reconnaissance Techniques
- System Hacking Phases and Attack Techniques
- Network and Perimeter Hacking
- Web Application Hacking
- Wireless Network Hacking
- Mobile Platform, IoT, and OT Hacking
- Cloud Computing
- Cryptography
8. GIAC Security Essentials Certification (GSEC)

The GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC) is an entry-level certification that validates knowledge of information security concepts and terminology.
GSEC features
| Cost | $849 |
| Exam duration | 4 hours |
| Number of questions | 180 |
| Passing grade | 73% |
| Valid for | 4 years |
| Requirements | None |
Who is GSEC for?
GSEC is for a wide range of security professionals, including system administrators, network administrators, and security officers. It can be too technical for managers, but it is worth considering if you want to get more technical experience.
GSEC domain
The GSEC certification covers the following topics:
- Active defense, defense in depth, access control & password management
- Cryptography
- Defensible network architecture
- Incident handling & response
- Linux and Windows security
- Security policy
- Web communication security
9. Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK)
Best certification for cloud security

The Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK) is a certificate that proves skills in securing cloud services. The CCSK is a broad overview of cloud security and will help you understand things like data security, key management, and identity and access management.
Unlike other cybersecurity tests, CCSK is open book. However, don't underestimate how hard the exam is. Only 62% of people pass.
CCSK features
| Cost | $395 |
| Exam duration | 90 minutes |
| Number of questions | 60 |
| Passing grade | 80% |
| Valid for | No expiration |
| Requirements | None |
Who is CCSK for?
The CCSK is a certification for IT professionals who work with cloud computing. It's a good idea to get this certification if you're a security professional, because you will learn a lot about cloud security. But other IT professionals can benefit from it too, like developers, IT ops, and audit/compliance staff.
CCSK domain
CCSK covers the following topics:
- Cloud Computing Fundamentals
- Data Security for Cloud Computing
- Infrastructure Security for Cloud Computing
- Application Security and Identity Management for Cloud Computing
- Managing Cloud Security and Risk
- Cloud Security Operations
10. Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
The SSCP certification is a globally recognized IT security certification that proves the holder has the technical skills and knowledge to secure an IT infrastructure.
The SSCP's focus is on the technical aspects of information security.
SSCP Features
| Cost | $249 |
| Exam duration | 3 hours |
| Number of questions | 125 |
| Passing grade | 700/1000 |
| Valid for | No expiration |
| Requirements | None |
| Standard | ANSI/ISO/IEC Standard 17024 |
Who is SSCP for?
The SSCP is a for hands-on practitioners who monitor information systems to protect against security threats. It also tests the skill to use security tools and procedures to react to security incidents. The hands-on focus of this certification makes it ideal for system administrators, programmers, DBAs, and systems analysts.
SSCP Domains
SSCP covers the following seven domains:
- Security Operations and Administration
- Access Controls
- Risk Identification, Monitoring and Analysis
- Incident Response and Recovery
- Cryptography
- Network and Communications Security
- Systems and Application Security
11. Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
Best advanced cloud security certification
The CCSP credential certifies that you have the knowledge and skills necessary to keep data safe in the cloud. The credential covers design, implementation, architecture, operations, controls, and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
CCSP features
| Cost | $599 |
| Exam duration | 3 hours |
| Number of questions | 125 |
| Passing grade | 700/1000 |
| Valid for | 3 years |
| Requirements | 5 years of experience |
| Standard | ANSI/ISO/IEC Standard 17024 |
Who is CCSP for?
CCSP is for experienced professionals who work in cloud security. The certification is for enterprise architects, systems engineers, systems architects, security administrators, and IT and information security leaders.
CCSP domains
CCSP covers the following six domains:
- Cloud Concepts, Architecture and Design
- Cloud Data Security
- Cloud Platform & Infrastructure Security
- Cloud Application Security
- Cloud Security Operations
- Legal, Risk and Compliance
FAQ on Cybersecurity Certifications
Who is an ethical hacker?
A certified ethical hacker is a professional who specializes in attacking computer systems and networks. They understand how to find and exploit vulnerabilities in toin access to critical data. Certified ethical hackers have permission from system owners to hack into systems. They take precautions to ensure the outcomes remain confidential.
The difference between ethical and unauthorized hacking is that ethical hackers are allowed to hack, while unauthorized hackers often break the law.
Vendor-neutral vs. Vendor-specific
There are two types of cybersecurity certifications:
- Vendor-neutral certifications are not tied to any specific company or product, while
- vendor-specific certifications are tied to a particular company or product.
Many people prefer vendor-neutral certifications because they provide broader knowledge and skills that can be applied to multiple companies and products. Vendor-specific certifications, on the other hand, provide in-depth knowledge of a particular company or product.
Resources
Furnell, Steven. "The cybersecurity workforce and skills." Computers & Security 100 (2021): 102080.
(ISC)2 2019 (ISC)2. Strategies for Building and Growing Strong Cybersecurity Teams: (ISC)2 Cybersecurity Workforce Study, 2019, https://www.isc2.org/-/media/ISC2/Research/2019-Cybersecurity-Workforce-Study/ISC2-Cybersecurity-Workforce-Study-2019.ashx
James, Jason E., and Jennifer Callen. "CYBERSECURITY CERTIFICATIONS MATTER." Issues in Information Systems 19.3 (2018).
Marquardson, Jim, and Ahmed Elnoshokaty. "Skills, Certifications, or Degrees: What Companies Demand for Entry-Level Cybersecurity Jobs." Information Systems Education Journal 18.1 (2020): 22-28.
Summers, Timothy and Lyytinen, Kalle J. and Lingham, Tony and Pierce, Eugene A., How Hackers Think: A Study of Cybersecurity Experts and Their Mental Models (September 20, 2013). Third Annual International Conference on Engaged Management Scholarship, Atlanta, Georgia. September 19-22, 2013. Paper 3.3
Whitman, Michael E., and Herbert J. Mattord. Roadmap to information security: For IT and infosec managers. Cengage Learning, 2012.
Oakley, Jacob G. "The state of modern offensive security." Professional Red Teaming. Apress, Berkeley, CA, 2019. 29-41.
Josip Miskovic is a software developer at Americaneagle.com. Josip has 10+ years in experience in developing web applications, mobile apps, and games.
Read more posts →Last modified on:
- Certification Criteria
- 1. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- 2. Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
- 3. Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- 4. GIAC Information Security Fundamentals (GISF)
- 5. Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- 6. CompTIA Security+
- 7. Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- 8. GIAC Security Essentials Certification (GSEC)
- 9. Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK)
- 10. Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
- 11. Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
- FAQ on Cybersecurity Certifications
- Resources

I've used these principles to increase my earnings by 63% in two years. So can you.
Dive into my 7 actionable steps to elevate your career.
