URL vs URI Difference with Examples
What's the difference between URL and URI?
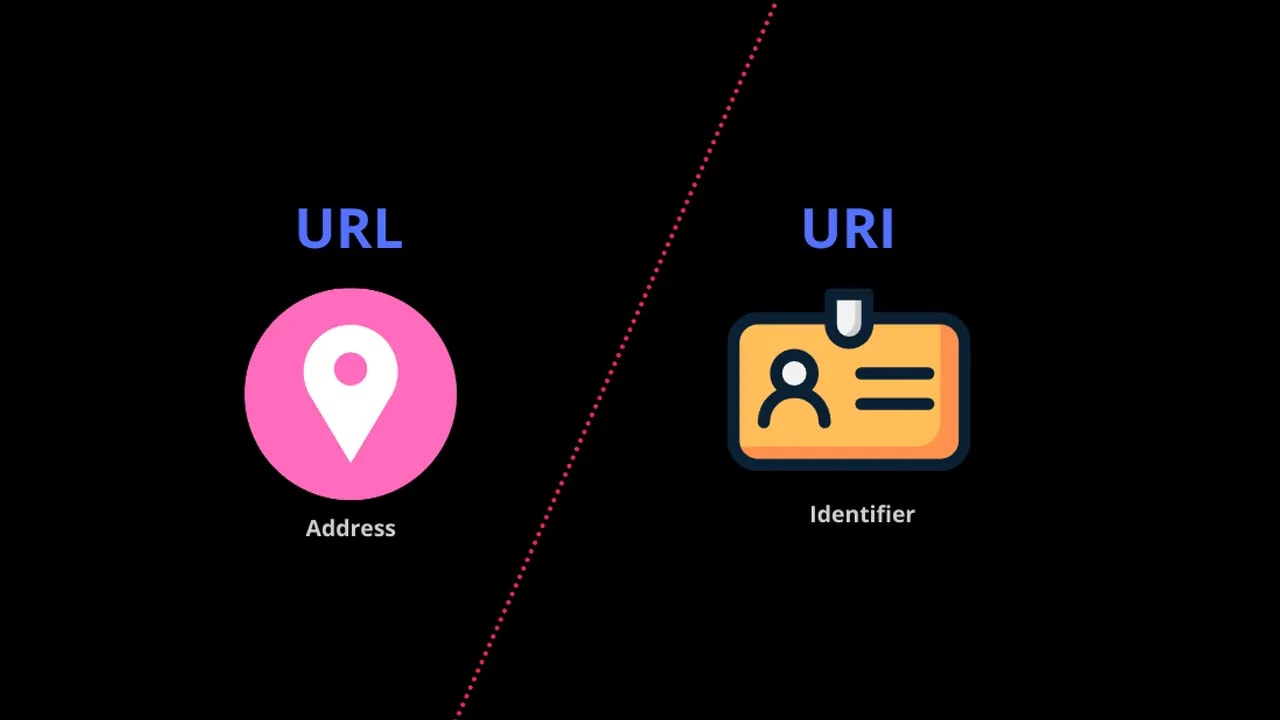
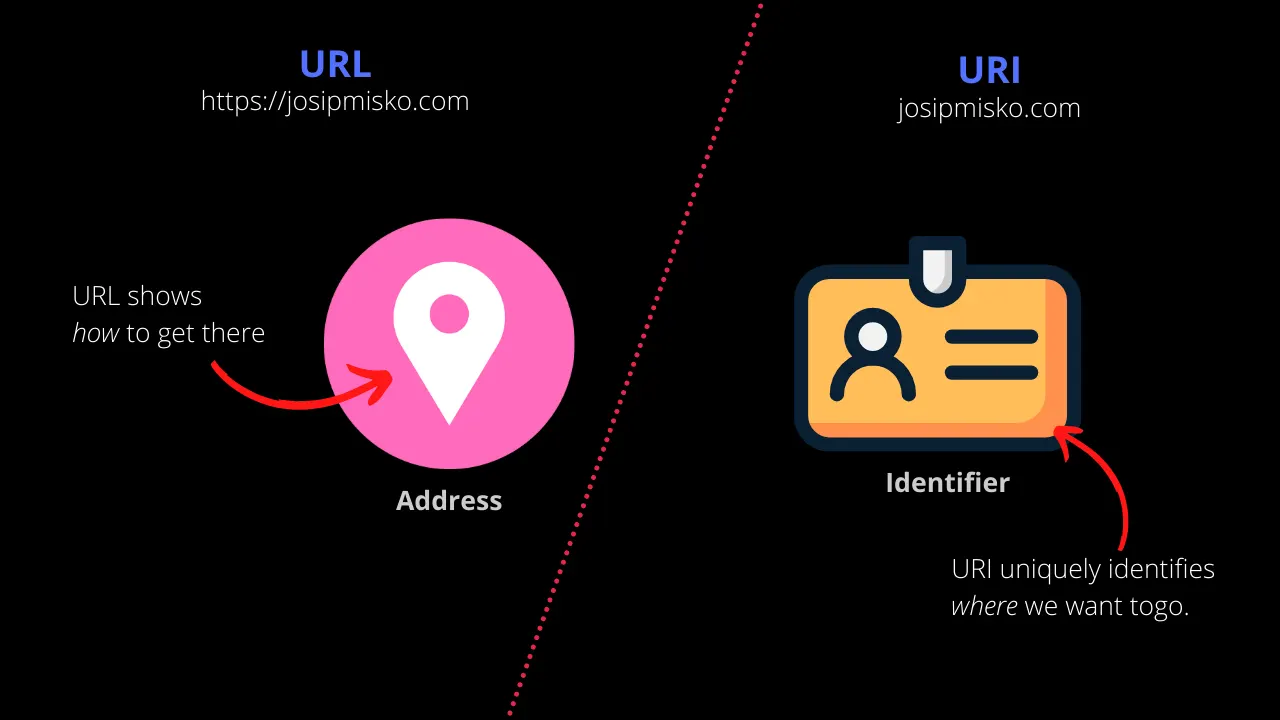
The main difference between URL and URI is that URL is an address, while a URI is an identifier. A URL locates a resource, while a URI uniquely identifies a resource.
URLs are mainly used to locate resources on the internet. On the other hand, URI can be used for other purposes, such as identifying people, places, things, or ideas. Moreover, a URL is a subset of a URI.
Unlike URLs, URIs are used to denote resources without any intention that they are accessed.
URL | URI |
|---|---|
Address | Identifier |
Locates a resource | Uniquely identifies a resource |
Subset of URI | Superset of URL |
Mainly used to locate resources on the internet. | Used to identifying people, places, things, or ideas. |
Example: https://google.com | Example: google.com |
URL vs URI - differences
What's the relationship between URL and URI?
URL is a subset of URI. All URLs are URI, but not all URI are URL.
URL schemes are the key differentiator between URL and URI because schemes describe how to locate a resource. There can be many ways we can access the same resource.
For example, we can access the same file using HTTPS and FTP protocols:
https://www.w3schools.com/images/w3schools_green.jpg
ftp://www.w3schools.com/images/w3schools_green.jpg
As we can see from the example above, both URL and URI are used to uniquely identify resources, but URL provides more information on how to locate and access the resource. Therefore, URL is a more specific type of URI.
URL
What is a URL?
A URL is a global address of documents and protocols that you can use to get resources on a computer network.
We use URLs to refer to:
- Web pages (HTTP):
https://josipmisko.com - Email addresses (mailto):
mailto: myname@josipmisko.com - Databases (JDBC):
jdbc:sqlserver://;serverName=testdb\\1;integratedSecurity=true; - File Transfer Protocols (FTP):
ftp://user@josipmisko.com/
Who created URL?
Tim Berners-Lee created the first URL in 1989. But it wasn't until 1994 that he, Larry M Masinter, and Mark P. McCahill wrote an RFC 1738 that gave a formal definition of what a URL is.
What's the structure of a URL?
URL has the following structure:
https://josipmisko.com:443/posts/url-vs-uri?source=campaign#url
URL part | Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|
https: | Scheme | Identifies protocol used to connect to the resource. |
josipmisko.com | Host | Name of a machine to connect to. |
443 | Server port | Identifies the server on the machine. |
posts/url-vs-uri | Path | Locates the content on the server. |
?source=campaign | Query parameters | Passes additional information. |
#url | Fragment | Identifies specific section of the content. |

URL structure.
URL schemes
URL schemes part is what differentiates URL from URI because scheme describes how to locate a resource.
The most popular scheme types are:
URL scheme | Name |
|---|---|
http | Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
ftp | File Transfer protocol |
gopher | Gopher protocol |
mailto | Electronic mail address |
URL Examples
Here's a list of URL examples:
http://www.w3schools.com/default.aspftp://user:password@hostname:21/pathname/filenamenews:comp.infosystems.www.servers.unixtelnet://hostname:23/file:///C:/WINDOWS/Start%20Menu/Programs/Accessories/Notepad.lnk
URI
What is a URI?
URI is a string of characters used to identify a name or a resource. The acronym stands for Uniform Resource Identifier.
URIs are global and they can be used to identify anything, including real-world objects, such as people and places, as well as abstract concepts.
An example of a URI is a book's International Standard Book Number (ISBN). This number is used to uniquely identify a book. The ISBN consists of numbers and dashes, and it looks like this: 978-0-306-40615-7.
The table below describes the acronym URI (Uniform Resource Identifier):
URI acronym part | Description |
|---|---|
Uniform | Uniformity means that we can use different identifiers in the same way, even if the way we access them is different. This allows for a uniform interpretation of the meaning of common syntactic conventions across different identifiers. |
Resource | According to RFC2396, a "resource" is anything that a URI can identify. |
Identifier | An identifier is information that you need to tell one resource apart from all other resources. |
URI Examples
Here's a list of URI examples:
- ISBN: 978-0-306-40615-7
- DOI: 10.1000/182
- URN: urn:isbn:978-0-306-40615-7
https://google.com
URL vs URI Summary
URL and URI have many differences:
- A URL is an address, while a URI is an identifier.
- A URL locates a resource, while a URI uniquely identifies the resource.
- URL is a subset of URI. All URLs are URI, but not all URIs are URL.
- URLs are mainly used to locate resources on the internet, while URI can also be used for other purposes, such as identifying people, places, things, or ideas.
- Unlike URLs, URIs are used to denote resources without any intention that they are accessed.
- URL is a type of URI. URI is the superset of URL.
URL vs URI FAQ
What is a resource?
A resource is anything that can be identified by a URI. This includes websites, books, people, places, and other things. The term "resource" is used in a general sense and does not imply anything about how the resource can be accessed.
What are the three main parts of the URL?
The three main parts of a URL are the scheme, authority, and path:
- The scheme is the part of the URL that indicates what protocol is being used. The most common schemes are HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and file.
- The authority is the part of the URL that indicates who or what is responsible for the resource being requested. The authority is typically in the form of a domain name, but can also be an IP address.
- The path is the part of the URL that indicates where the resource is located. The path typically includes the file name of the resource being requested.
For example, in the URL http://www.example.com/index.html, the scheme is HTTP, the authority is www.example.com, and the path is /index.html.
What is a query string?
A query string is a part of a URL that typically contains information that is used to retrieve specific resources from a server.
Query strings are typically used in URL s that point to web pages that display query results, such as search results pages.
For example, if you perform a search on a website for "books about cats", the URL of the resulting page may look something like this:
http://www.example.com/search?q=books+about+cats
In this URL, the query string is q=books+about+cats. The value of the query string (in this case, "books about cats") is passed to a server, which then uses that value to determine which resources to return.
What is URI in REST API?
URIs are important for REST APIs because they provide a way to identify resources. A URI can be used to identify a resource in many different ways, including by its name, location, or id number. By using URIs, REST APIs can provide a consistent way to access resources that is independent of the underlying implementation.
REST APIs use HTTP methods to indicate the action to be performed on a given resource. The most common HTTP methods are GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
This is a commonly asked REST API Interview question.
Read more: REST API Best Practices
Sources
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc2396
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc3986
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc1630.html
Josip Miskovic is a software developer at Americaneagle.com. Josip has 10+ years in experience in developing web applications, mobile apps, and games.
Read more posts →Last modified on:
- What's the difference between URL and URI?
- What's the relationship between URL and URI?
- URL
- What is a URL?
- Who created URL?
- What's the structure of a URL?
- URL schemes
- URL Examples
- URI
- What is a URI?
- URI Examples
- URL vs URI Summary
- URL vs URI FAQ
- What is a resource?
- What are the three main parts of the URL?
- What is a query string?
- What is URI in REST API?
- Sources

I've used these principles to increase my earnings by 63% in two years. So can you.
Dive into my 7 actionable steps to elevate your career.